WASTE MANAGEMENT IN KOSOVO[1]
Waste is one of the main environmental pollutants in the world we live in. It is generated by the daily activities of individuals, families, businesses, and various producers. Inadequate waste management poses serious risks to human health, the environment, and overall living conditions. To eliminate these risks, it is necessary to establish waste management systems. This includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from the moment it is generated to its final disposal. In Kosovo, waste management is regulated by Law No. 04/L-060 on Waste, adopted in 2012. The purpose of this law is to prevent and minimize waste generation as much as possible, to reuse usable components from waste, to promote sustainable development by protecting and preserving natural resources, to prevent the negative impacts of waste on the environment and human health, and to ensure environmentally acceptable final waste disposal. Waste management is also regulated through other sub-legal acts issued by the ministry. The diagram represents the basic functioning of the municipal solid waste collection chain in Kosovo. Waste is collected by waste generators through operators who provide the service, gathered by them, and then transported either to transfer stations (in some municipalities) or directly to permanent disposal at central landfills.
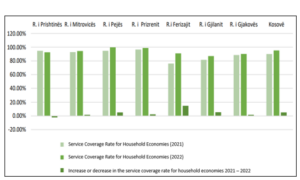
Service Coverage
The basic service of collecting and transporting municipal waste and transferring it to sanitary landfills for disposal in municipalities is carried out by licensed public and private operators. The following figure shows the level of service coverage for municipal waste collection by region, specifically by municipality.
Wild Dumps
The environmental condition in Kosovo is significantly affected by the phenomenon of illegal dumpsites. According to their size, they are classified into three categories: large, medium, and small. This classification is based on visually assessing the volume of the dumps. In terms of waste composition, dumpsites are classified as: (a) municipal waste dumpsites; (b) construction and demolition waste dumpsites; (c) hazardous waste dumpsites; (d) bulky waste dumpsites; and (e) other types of waste dumpsites. In June 2023, a registration of illegal dumpsites was carried out in 38 municipalities, where a total of 746 illegal dumpsites of various sizes and compositions were registered.
The disposal of municipal waste
AMMK has secured data from the management of 7 sanitary landfills regarding the amount of waste disposed of during the year 2022. Based on this data, and comparing it with previous years, we can observe that the trend of waste disposal is continuously increasing. In 2022, the amount of waste disposed of, compared to 2021, showed an increase of 12,932.36 tons, or a 2.6% increase overall across all landfills. In the landfills managed by KMDK, the amount of waste disposed of in 2022 was 386,533.29 tons/year, marking a 2.8% increase compared to 2021. Meanwhile, in other sanitary landfills managed by KRM, the amount of waste disposed of was 116,354.49 tons/year, an increase of 2% compared to 2021. In total, the amount of municipal waste disposed of in sanitary landfills reached 502,887.72 tons/year.
Source separation of waste
Integrated recycling management is a challenge. Waste separation at the source remains one of the aspects of waste management where municipalities have not yet taken steps to implement this step, which is key to the start of integrated waste management. In the absence of source separation, a sustainable waste recycling system, which is one of the main components of circular economy development, cannot be developed. Based on the analysis of data reported by municipalities and operators for waste management in 2022, as well as in previous years, it has been assessed that almost no municipality has taken concrete steps toward the separate collection of waste. In Kosovo, there are several operators that deal with recycling a portion of waste (mainly nylon, plastic, textiles, and paper). However, there are no reported data on the level of recycling, although AMMK has estimated that approximately 3% of the waste generated in Kosovo is recycled by these operators annually.
PROPOSED WASTE MANAGEMENT
Based on the latest data, we can conclude that Kosovo needs to start and implement better waste management practices to prevent waste from ending up in landfills. According to the data on the composition of disposed waste, it consists of 22% other waste, 33% recyclable waste, and 45% compostable waste.
Collection – Initially, a waste separation process at the source should be implemented, including households, businesses, and all waste producers. This separation would enable a more structured and efficient treatment of waste, significantly reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. Another important step is the creation of a digital platform or application which would serve as a communication tool between citizens and municipal waste management services. This application would inform citizens about the days and locations for the collection of different categories of waste, such as plastic, glass, organic waste, and more.
Transportation – Waste should be transported to treatment sites to prevent pollution during transit.
Waste Treatment – This includes recycling, composting, and energy production to reduce environmental impact.
- Recycling – Recyclable materials will be sent to companies that handle their recycling.
- Composting – Organic waste will be sent to a site where it will be transformed into natural fertilizer, which will then be used to improve soil quality.
- Energy Production – Non-recyclable waste will be incinerated to generate energy.
Landfilling – Waste that cannot be treated will end up in landfills, but only a small portion of it.
[1] This designation is without prejudice to positions on status, and is in line with UNSCR 1244/1999 and the ICJ Opinion on the Kosovo declaration of independence.








